Despite a turbulent year, global intangible value is now at an all-time high of US$ 65.7 trillion.
Our annual 2020 Global Intangible Finance Tracker (GIFT) study ranks the top global companies by total intangible value. Over US$10 trillion of this resides in the top 10 - Apple, Amazon, Aramco, Microsoft, Alphabet, Facebook, Alibaba, Tencent, Tesla and VISA.
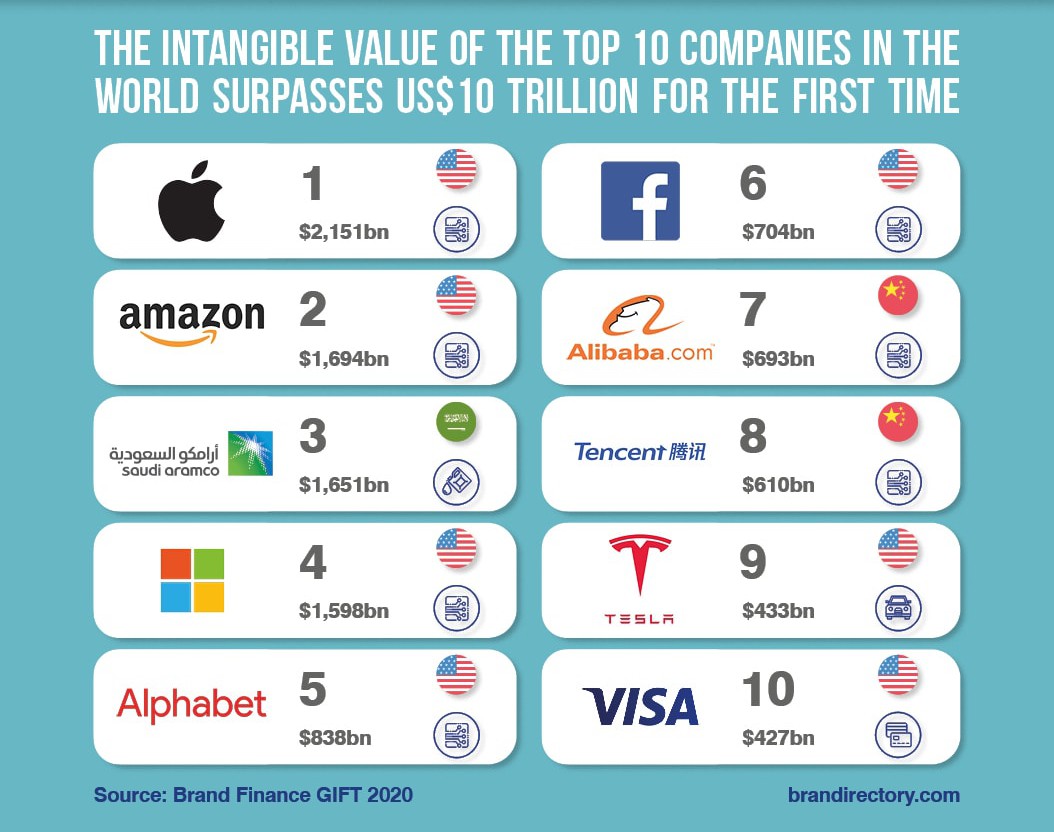
The American representation on this list plays a role in the USA being the most intangible country in the world, with Denmark in 2nd and Ireland in 3rd place. Countries which are more intangible are more attractive to investors, due to the reputation and innovation of the companies that reside there.
Some sectors have been particularly hard-hit by COVID-19 – Airlines and Insurance as a whole have both lost intangible value since the beginning of 2020.
Read more: Covid 19 - Brand Value and Leadership in Times of Crisis
Due to last year’s major merger of Raytheon and United Technologies, Aerospace & Defence is now the most intangible sector – 20% of the total sector value is represented on balance sheets as acquired goodwill.
Intangible Value and Goodwill
Goodwill is the balancing figure between the money paid for a company and the fair value of the assets acquired. Therefore, goodwill is seen as the intertwined value of know-how, synergies and reputation.
Subsequently, companies are supposed to revalue the company they acquired to check if its fallen. If it has, they may need to impair the value of goodwill on their balance sheet. Impairment suggests that company performance is worse than expected, so perhaps that manager overpaid for the acquisition.
Not many people that I know want to admit they overpaid for anything so where possible, goodwill tends to be left as is. This is one among many issues with the current state of intangible asset reporting explored in the Brand Finance GIFT 2020 report.
Click here to access the full Global Intangible Finance Tracker (GIFT) report
